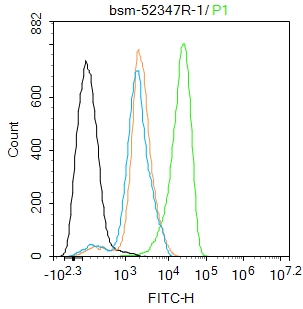
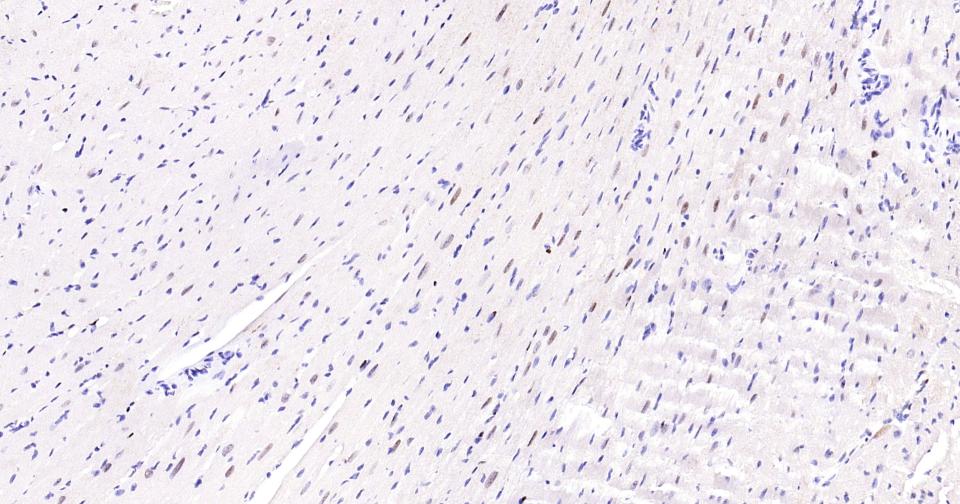
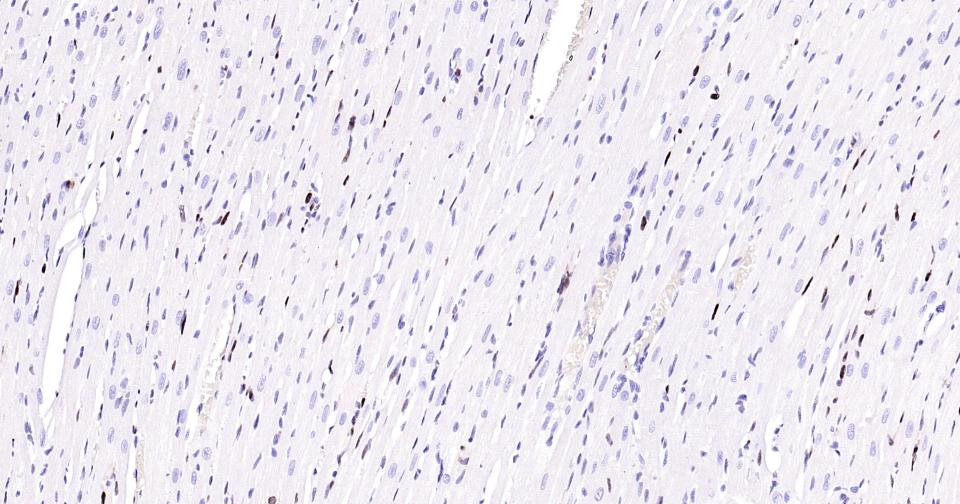
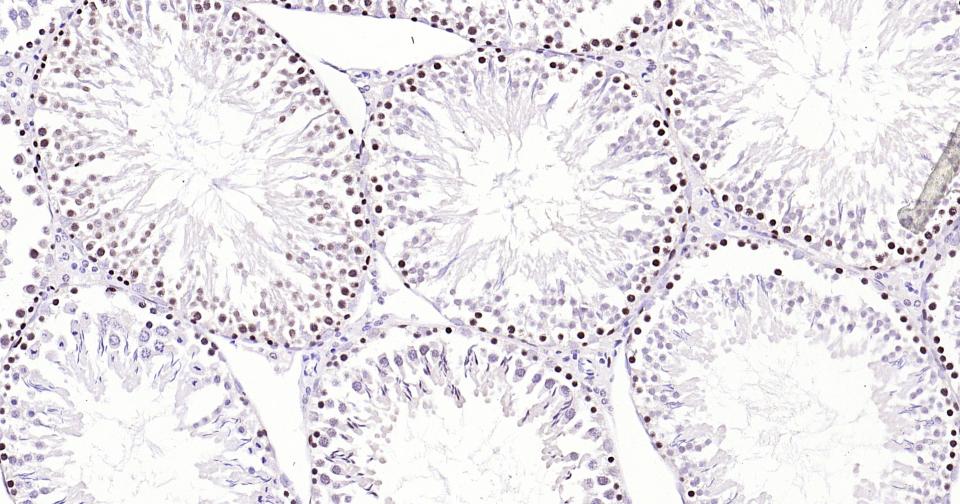
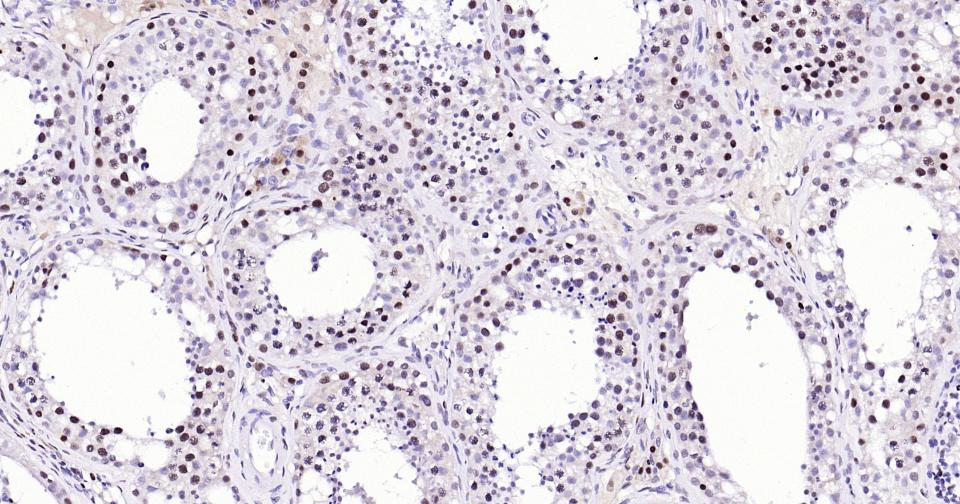
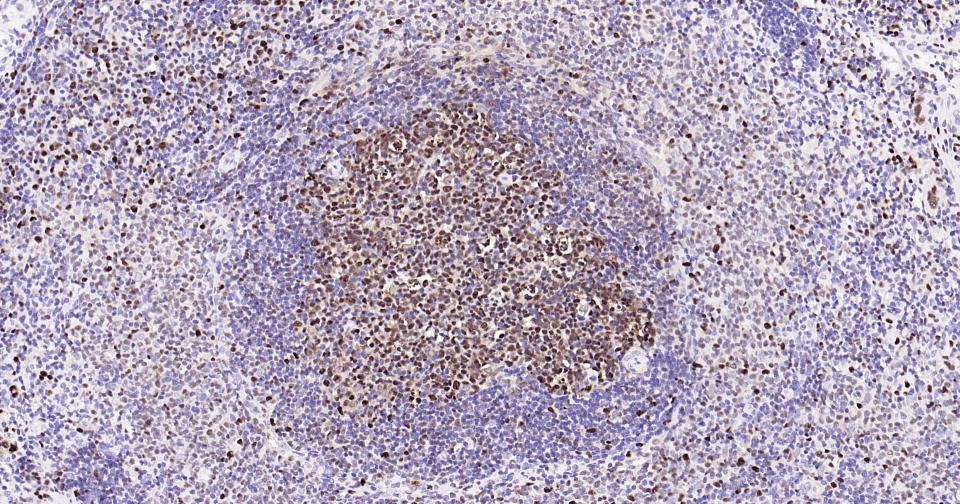
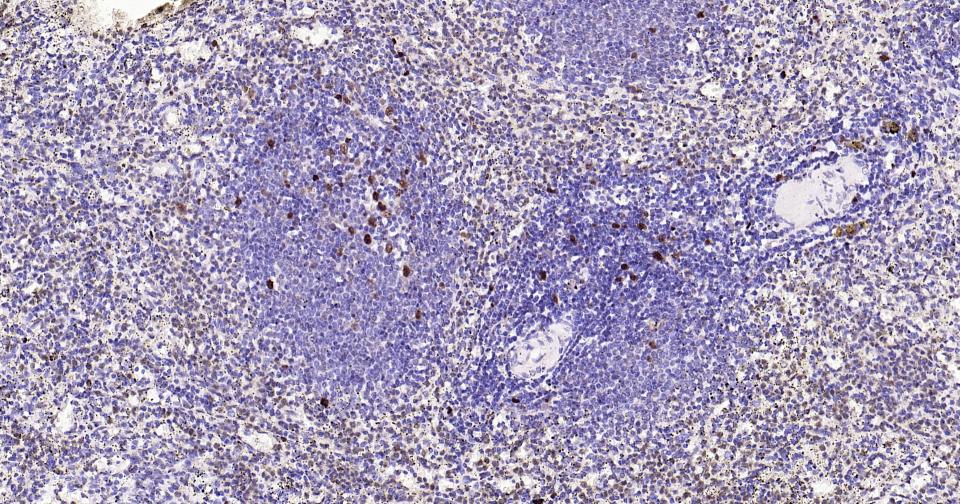
PCNA Recombinant Rabbit mAb, Nuclear Loading Control
PCNA Recombinant Rabbit mAb, Nuclear Loading Control
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IHC-F, IF, ICC |
|---|---|
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Recombinant |
| Calculated MW | 29 KDa |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human PCNA |
| Epitope Specificity | 100-160/261 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Nucleus. Note=Forms nuclear foci representing sites of ongoing DNA replication and vary in morphology and number during S phase. Together with APEX2, is redistributed in discrete nuclear foci in presence of oxidative DNA damaging agents. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the PCNA family. |
| SUBUNIT | Homotrimer (PubMed:24939902).Interacts with p300/EP300; the interaction occurs on chromatin in UV-irradiated damaged cells (PubMed:24939902).Interacts with CREBBP (via transactivation domain and C-terminus); the interaction occurs on chromatin in UV-irradiated damaged cells (PubMed:24939902).Directly interacts with POLD1, POLD3 and POLD4 subunits of the DNA polymerase delta complex, POLD3 being the major interacting partner; the interaction with POLD3 is inhibited by CDKN1A/p21(CIP1) (PubMed:11595739, PubMed:16510448, PubMed:22148433, PubMed:24939902).Forms a complex with activator 1 heteropentamer in the presence of ATP. Interacts with EXO1, POLH, POLK, DNMT1, ERCC5, FEN1, CDC6 and POLDIP2 (PubMed:9305916, PubMed:9302295, PubMed:9566895, PubMed:11784855, PubMed:12522211, PubMed:15225546, PubMed:15149598, PubMed:24911150, PubMed:15616578).Interacts with APEX2; this interaction is triggered by reactive oxygen species and increased by misincorporation of uracil in nuclear DNA (PubMed:11376153, PubMed:19443450).Forms a ternary complex with DNTTIP2 and core histone (PubMed:12786946).Interacts with KCTD10 and PPP1R15A (By similarity).Interacts with SMARCA5/SNF2H (PubMed:15543136).Interacts with BAZ1B/WSTF; the interaction is direct and is required for BAZ1B/WSTF binding to replication foci during S phase (PubMed:15543136).Interacts with HLTF and SHPRH (PubMed:17130289, PubMed:18316726, PubMed:18719106).Interacts with NUDT15; this interaction is disrupted in response to UV irradiation and acetylation (PubMed:19419956).Interacts with CDKN1A/p21(CIP1) and CDT1; interacts via their PIP-box which also recruits the DCX(DTL) complex. The interaction with CDKN1A inhibits POLD3 binding (PubMed:11595739, PubMed:16949367, PubMed:18794347, PubMed:18703516).Interacts with DDX11 (PubMed:18499658).Interacts with EGFR; positively regulates PCNA (PubMed:17115032).Interacts with PARPBP (PubMed:22153967).Interacts (when ubiquitinated) with SPRTN; leading to enhance RAD18-mediated PCNA ubiquitination (PubMed:22681887, PubMed:27084448).Interacts (when polyubiquitinated) with ZRANB3 (PubMed:22704558, PubMed:22705370, PubMed:22759634).Interacts with SMARCAD1 (PubMed:21549307).Interacts with CDKN1C (PubMed:22634751).Interacts with PCLAF (via PIP-box) (PubMed:21628590, PubMed:23000965).Interacts with RTEL1 (via PIP-box); the interaction is direct and essential for the suppression of telomere fragility (PubMed:24115439).Interacts with FAM111A (via PIP-box); the interaction is direct and required for PCNA loading on chromatin binding (PubMed:24561620).Interacts with LIG1 (PubMed:24911150).Interacts with SETMAR (PubMed:20457750).Interacts with ANKRD17 (PubMed:23711367).Interacts with FBXO18/FBH1 (via PIP-box); the interaction recruits the DCX(DTL) complex and promotes ubiquitination and degradation of FBXO18/FBH1 (PubMed:23677613).Interacts with POLN (PubMed:19995904).Interacts with SDE2 (via PIP-box); the interaction is direct and prevents ultraviolet light induced monoubiquitination (PubMed:27906959).Component of the replisome complex composed of at least DONSON, MCM2, MCM7, PCNA and TICRR; interaction at least with PCNA occurs during DNA replication (PubMed:28191891).Interacts with MAPK15; the interaction is chromatin binding dependent and prevents MDM2-mediated PCNA destruction by inhibiting the association of PCNA with MDM2 (PubMed:20733054).Interacts with PARP10 (via PIP-box) (PubMed:24695737).Interacts with DDI2 (PubMed:29290612).Interacts with HMCES (via PIP-box) (PubMed:30554877).Interacts with TRAIP (via PIP-box) (PubMed:27462463, PubMed:26711499).Interacts with UHRF2 (PubMed:28951215).Interacts with ALKBH2; this interaction is enhanced during the S-phase of the cell cycle. Interacts with ATAD5; the interaction promotes USP1-mediated PCNA deubiquitination (PubMed:20147293).By Similarity51 Publications(Microbial infection) Interacts with herpes virus 8 protein LANA1. |
| Post-translational modifications | Following DNA damage, can be either monoubiquitinated to stimulate direct bypass of DNA lesions by specialized DNA polymerases or polyubiquitinated to promote recombination-dependent DNA synthesis across DNA lesions by template switching mechanisms. Following induction of replication stress, monoubiquitinated by the UBE2B-RAD18 complex on Lys-164, leading to recruit translesion (TLS) polymerases, which are able to synthesize across DNA lesions in a potentially error-prone manner. An error-free pathway also exists and requires non-canonical polyubiquitination on Lys-164 through 'Lys-63' linkage of ubiquitin moieties by the E2 complex UBE2N-UBE2V2 and the E3 ligases, HLTF, RNF8 and SHPRH. This error-free pathway, also known as template switching, employs recombination mechanisms to synthesize across the lesion, using as a template the undamaged, newly synthesized strand of the sister chromatid. Monoubiquitination at Lys-164 also takes place in undamaged proliferating cells, and is mediated by the DCX(DTL) complex, leading to enhance PCNA-dependent translesion DNA synthesis. Sumoylated during S phase.Acetylated in response to UV irradiation. Acetylation disrupts interaction with NUDT15 and promotes degradation.Phosphorylated. Phosphorylation at Tyr-211 by EGFR stabilizes chromatin-associated PCNA. |
| DISEASE | A neurodegenerative disorder due to defects in DNA excision repair. ATLD2 is characterized by developmental delay, ataxia, sensorineural hearing loss, short stature, cutaneous and ocular telangiectasia, and photosensitivity. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is a 28kDa nuclear protein associated with the cell cycle, a nuclear protein vital for cellular DNA synthesis. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen was originally identified by immunofluorescence as a nuclear protein whose appearance correlated with the proliferate state of the cell. PCNA is required for replication of DNA in vitro and has been identified as the auxiliary protein (cofactor) for DNA polymerase delta. The anti-PCNA antibodies react with the nuclei of proliferating cells. PCNA is essential for cellular DNA synthesis and is also required for the in vitro replication of simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA where it acts to coordinate leading and lagging strand synthesis at the replication fork. The PCNA protein may fulfil several separate roles in the cell nucleus associated with changes in its antigenic structure. |
| Dilution | WB=1:1000-10000,IHC-P=1:200-1000,IHC-F=1:200-1000,ICC/IF=1:100-500,IF=1:200-1000,Flow-Cyt=1ug/Test |
|---|---|
| Format | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4), 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide and 50% Glyce |
| Storage | Store at -20 ℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 ℃. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.




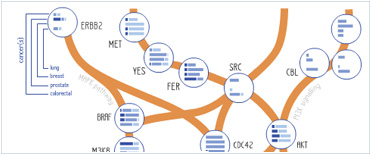







 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.